Lean Results PRO - FAQ
Our Lean Results PRO online course covers a range of topics from explaining why you should implement lean and it's benefits, how to successfully and practically implement the lean approach and how to measure the results of a successful lean implementation. This page outlines some of the topics covered in the Lean Results PRO course to give you a more detailed understanding of how implementing lean can benefit your team or business.

Who is this online course for?
The Lean Results PRO course is designed for professionals who want to go beyond Lean theory and apply it effectively in real work environments. It’s ideal for people working in technical and operational fields such as manufacturing, logistics, IT, or healthcare, who need clear, practical guidance to transform concepts into results.
Whether you’re a Production or Maintenance Manager, Continuous Improvement Agent, Healthcare or IT Coordinator, Team Leader, or even a Plant Manager looking to empower your teams, this course helps you make Lean work for your specific context and show improved results.
If you’ve ever read about Lean but struggled to put it into action — to connect tools, identify wastes, choose the right methods, and build a structured improvement plan — Lean Results PRO gives you the roadmap you’ve been missing.
Through:
° Step-by-step explanations of Lean tools (5S, SMED, Kanban, Standard Work, and more),
° Hands-on examples from shop floors,
° Ready-to-use templates and practical guides,
° The opportunity to discuss your challenges and get personalized guidance.
You’ll be able to turn Lean concepts into daily improvement habits that drive measurable results in your processes.
Whether you’re starting your Lean journey or seeking to sharpen your team’s skills, Lean Results PRO will help you bridge the gap between theory and practice — so you can confidently lead change, optimize performance, and build a stronger continuous improvement culture.
If you'd like to book a call to clarify any doubt or see how can we support you in your Lean journey, you can contact us per email: [email protected]
Also, you can visit our YouTube channel and subscribe to receive alerts of new videos releases: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is a lean culture?
Lean culture refers to a set of values, principles, and practices within an organization that align with the principles of lean thinking. At its core, lean culture is a mindset and approach that emphasizes continuous improvement, waste reduction, and employee empowerment. Originating from the lean manufacturing philosophy pioneered by Toyota, lean culture has expanded beyond its manufacturing roots and is now applied across various industries and sectors.
Key characteristics of a lean culture include:
Continuous Improvement
A commitment to ongoing enhancement of processes, products, and services. Employees are encouraged to identify inefficiencies and actively participate in finding solutions for improvement. Continuous improvement training is included in the Lean Results PRO course.
Waste Elimination
The relentless pursuit of eliminating waste in all its forms, including time, materials, and resources. This involves scrutinizing every aspect of the workflow to identify and eliminate non-value-added activities.
Respect for People
A fundamental principle of lean culture is the respect for every individual within the organization. This involves recognizing the unique skills, perspectives, and contributions of each employee.
Empowerment
Employees are empowered to make decisions and take ownership of their work. This empowerment fosters a sense of responsibility and engagement, contributing to the overall success of the organization.
Customer Focus
Prioritizing customer needs and delivering value are central tenets of lean culture. Organizations strive to understand customer requirements and align their processes to meet or exceed those expectations.
Visual Management
Using visual cues and tools to make information about processes, performance, and goals readily available. This helps in creating transparency and facilitating better communication within the organization.
Teamwork and Collaboration
Lean culture promotes a collaborative environment where cross-functional teams work together to achieve common goals. Collaboration is essential for addressing complex challenges and driving continuous improvement.
Standardization
Establishing standardized work processes and procedures to ensure consistency and efficiency. Standardization provides a baseline for improvement efforts and helps in sustaining positive changes over time.
Learn about Lean Culture with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
Advantages of lean manufacturing with lean culture
Lean manufacturing is a systematic approach to improving process efficiency by eliminating waste. Lean culture is a set of values and principles that support lean manufacturing by empowering employees to identify and eliminate waste, and to continuously improve processes.
The advantages of lean manufacturing with lean culture include:
Reduced waste
Lean culture encourages employees to identify and eliminate waste from all aspects of the manufacturing process (DOWNTIME): defects, over production, waiting, utilised talent, transportation, inventory, motion and extra processing.
Improved quality
Lean culture emphasizes the importance of quality in all aspects of the manufacturing process. By identifying and addressing the root causes of defects, businesses can improve the quality of their products.
Increased productivity
By eliminating waste and streamlining processes (information, material and product flows), lean culture can help businesses to produce more products within the customer requirements with fewer resources.
Reduced costs
Lean culture can help businesses to reduce costs by reducing waste, improving efficiency, and increasing productivity.
Improved customer satisfaction
By delivering high-quality products on time and at a competitive price, lean culture can help businesses to improve customer satisfaction.
In addition to these advantages, lean culture can also lead to improved employee morale, increased safety, and a more sustainable business.
Overall, lean manufacturing with lean culture can help businesses to improve their bottom line and become more competitive.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What does Lean Results Pro do?
Lean Results Pro is an online course dedicated to teaching lean methodology, empowering individuals and organizations to thrive in today's competitive landscape. Here's what our course offers:
·The Lean Approach: Navigate through the Lean principles, 8 types of waste and how the right mindset is so important for a Lean implementation project to succeed.
·Why Should We Implement Lean?: Explore the benefits of this methodology implementation, both for your team as for the business.
·Lean Culture: Learn how to foster a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration within your team .
·How to Provide a Collaborative Learning Environment: Discover strategies for creating an environment that encourages innovation and knowledge-sharing.
·Lean Tools: Per tool you can find a step-by-step on how to apply it on the shop floor as well the necessary templates to use. With no hassel, ready to use!
·Presenting Results: Master the art of measuring and communicating the impact of lean initiatives to stakeholders effectively.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
Why choose Lean Results Pro?
Considering enrolling in Lean Results Pro? Here's why it's the right choice for you:
·Comprehensive Learning Experience: Lean Results Pro offers a comprehensive curriculum covering all aspects of lean methodology, ensuring you gain a thorough understanding of key principles and practices.
·Expertly Crafted Content: Developed by industry experts, our course features meticulously crafted content designed to provide you with practical insights and actionable strategies for success.
·Practical Applications: Gain hands-on experience with real-world examples and case studies, allowing you to apply lean principles directly to your organization's challenges and opportunities.
·Lifetime Membership: Enjoy lifetime access to course materials and updates, allowing you to revisit content as needed and stay current with the latest trends and best practices in lean methodology.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
How will you benefit from Lean Results Pro?
Embark on a transformative learning journey with Lean Results Pro and unlock a multitude of benefits:
·Enhanced Skill Set: Acquire valuable skills and knowledge in lean methodology, empowering you to optimize processes, eliminate waste, and drive efficiency within your organization.
·Career Advancement: Gain a competitive edge in your field and open doors to new career opportunities by mastering lean principles and demonstrating your expertise to employers.
·Increased Productivity: Learn how to streamline workflows and improve productivity across your organization, allowing you to achieve more with less effort and resources.
·Empowered Teams: Foster a culture of collaboration, innovation, and accountability within your team, empowering members to contribute their best and drive collective success.
·Measurable Results: Learn how to collect, measure, and present results from lean initiatives, enabling you to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and showcase the impact of your efforts.
Who is Lean Results Pro for?
Wondering if Lean Results Pro is right for you? Here's who our course is designed for:
·Professionals in Project Management: Whether you're a seasoned project manager or just starting out in the field, Lean Results Pro offers valuable insights and techniques to enhance your project management skills and drive success.
·Operations Managers: If you're responsible for optimizing processes and maximizing efficiency within your organization, Lean Results Pro can provide you with the tools and strategies needed to achieve your goals.
·Manufacturing Professionals: Lean methodology has long been used in manufacturing settings to improve quality, reduce waste, and increase productivity. Lean Results Pro offers tailored guidance for manufacturing professionals looking to implement lean principles in their operations.
·Business Owners and Entrepreneurs: For business owners and entrepreneurs seeking to gain a competitive edge and drive growth in their organizations, Lean Results Pro offers practical solutions and best practices for implementing lean methodology.
·Anyone Interested in Continuous Improvement: Whether you work in healthcare, finance, technology, or any other industry, if you're passionate about driving continuous improvement and achieving excellence in your work, Lean Results Pro is for you.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
Are there any prerequisites for enrolling in Lean Results PRO?
No, you don't need any prerequisites to enroll in our course. Whether you're a complete beginner or have some familiarity with Lean methodology, our course is designed to cater to learners of all levels. We provide comprehensive explanations and step-by-step guidance to ensure that everyone can understand and benefit from the material, regardless of prior experience.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
Can I access the course materials on any device?
Absolutely! Our course materials are designed to be accessible from any device, including computers, tablets, and smartphones. As long as you have an internet connection, you can log in to our platform and access the content from wherever you are. Whether you prefer to study at your desk, on your couch, or even on the go, you'll have the flexibility to learn in a way that suits your lifestyle and preferences.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
Is there a money-back guarantee?
Yes, we offer a 30-day, 100% money-back guarantee to ensure your satisfaction with our course. We're confident that you'll find value in the content and delivery, but if for any reason you're not completely satisfied within the first 30 days of enrollment, simply reach out to our support team, and we'll promptly issue you a full refund, no questions asked. Your satisfaction is our priority, and we want you to feel confident in your decision to invest in your learning journey with us.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
Can I access the course materials indefinitely?
When you enroll in our course, you receive a lifetime membership, granting you indefinite access to the course materials. There's no expiration date or time limit, so you can progress through the content at your own pace and revisit it as often as you'd like. Whether you want to review a specific concept, refresh your knowledge, or delve deeper into a particular topic, you'll have the freedom to access the material whenever you need it, ensuring that your learning journey remains flexible and accommodating to your schedule.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is Kaizen?
Kaizen, which translates to "continuous improvement" in Japanese, is a Lean concept that emphasizes small, gradual improvements to processes.
By promoting staff engagement, ongoing education, data-driven decision-making, and group cooperation, Kaizen cultivates a culture of creativity and flexibility. With this strategy, companies are certain to positively change throughout time, tackling obstacles and grasping possibilities.
Through the promotion of a continuous improvement mindset, Kaizen enables teams to implement small, regular changes that, when added together, result in enhanced productivity, competitiveness, and long-term success.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
When Kaizen started?
Kaizen originated in post-World War II Japan, emerging as a response to the country's need for economic recovery and rebuilding. The concept evolved from various management philosophies and practices, including Total Quality Management and statistical process control.
Companies like Toyota played a significant role in popularizing Kaizen as a fundamental aspect of their Production System. Over time, Kaizen has become synonymous with continuous improvement and remains a cornerstone of lean manufacturing methodologies worldwide.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
How Kaizen can be implemented in an Organization?
Implementing Kaizen, the philosophy of continuous improvement, involves fostering a culture of innovation and employee involvement. Organizations encourage employees at all levels to identify and address inefficiencies through small, incremental changes.
This bottom-up approach empowers teams to take ownership of process improvements, leading to enhanced productivity and morale. By providing training, resources, and support, companies create an environment conducive to sustained Kaizen initiatives, driving continuous growth and adaptation.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
How to Sustain Kaizen in an Organization?
Sustaining Kaizen in your organization demands leadership alignment, employee engagement, and continuous learning. Establish standardized processes, encourage feedback, and celebrate successes. Continuous monitoring ensures progress and identifies improvement opportunities.
By embracing these strategies, organizations foster a culture of continuous improvement, driving innovation and long-term success.
Learn about Continuous Improvement with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What are Lean tools?
Lean tools are a broad category of approaches and procedures intended to find and remove waste, simplify operations, and promote ongoing development in businesses. They enable teams to systematically assess, optimize, and standardize workflows, which is crucial in accomplishing Lean objectives.
Examples of Lean tools include Value Stream Mapping, which visualizes the end-to-end flow of materials and information; 5S methodology, focusing on workplace organization and cleanliness; Kaizen events, facilitating rapid improvement initiatives; Just-in-Time (JIT) production, ensuring materials are delivered precisely when needed; Visual Management techniques, providing clear, visual cues to monitor and optimize processes; and Kanban systems, enabling efficient inventory
management, among others.
Organizations may optimize processes, increase quality, and cultivate a continuous improvement culture by correctly using Lean techniques.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
How to use Lean Tools?
Implementing Lean tools in your organization requires careful planning, strategic deploymen , and active engagement from all stakeholders. However, they always need to be implemented together with Lean Culture values/mindset. Only with peoples’ involvement can Lean tools have a good impact. Here are some key steps to effectively implement Lean tools:
Define Objectives: Clearly define the objectives and goals of implementing Lean tools in your organization.
· Assess Current State: Conduct a thorough assessment of the current state of your organization's processes and workflows.
· Select Appropriate Tools: Choose the most appropriate Lean tools and methodologies to address the identified areas for improvement.
· Pilot Testing: Pilot test Lean tools and methodologies in a controlled environment to assess their effectiveness and feasibility before full-scale implementation.
· Scale Up and Sustain: Establish standardized processes, provide ongoing support and guidance to employees, and continuously monitor and review performance to ensure sustained improvement over time.
Learn about Lean Tools with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is Kanban?
Kanban is a workflow management methodology that originated in Japan. It emphasizes visualizing work on a board, typically with columns representing different stages. Tasks, represented as cards, move through these stages. WIP limits are set for each stage to prevent overloading and maintain a smooth flow.
Learn about Kanban with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is 5S?
5S is a workplace organization methodology that originated in Japan. It comprises five principles aimed at improving efficiency, safety, and overall organization. The 5S framework includes:
Sort (Seiri)
Set in Order (Seiton)
Shine (Seiso)
Standardize (Seiketsu)
Sustain (Shitsuke)
5S is widely applied in manufacturing, service industries, and various workplaces to enhance organization, safety, and productivity. You can access 5S training in the Lean Results PRO course.
Learn about 5S with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is SMED?
SMED, or Single-Minute Exchange of Die, is a methodology focused on minimizing the time it takes to change over a manufacturing process from producing one product to another. The goal is to reduce setup or changeover time to a single-digit number of minutes, ideally within the range of one to ten minutes. SMED aims to increase operational efficiency, flexibility, and responsiveness in manufacturing.
By implementing SMED principles, organizations can achieve quicker changeovers, reduce production batch sizes, and improve overall production flexibility, allowing for more efficient and responsive manufacturing operations.
Learn about SMED with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
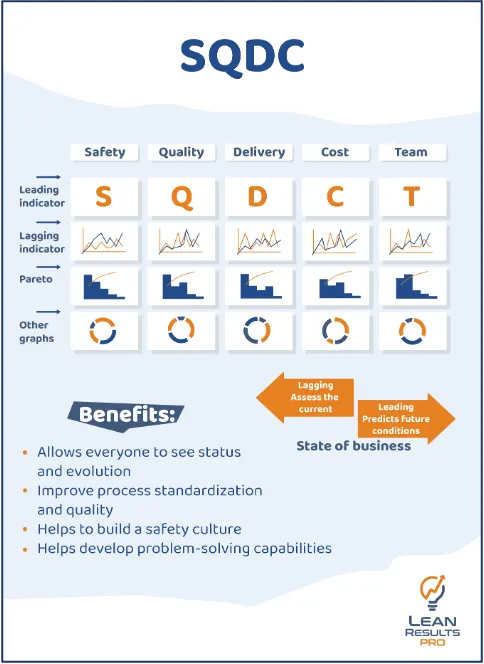
What are SQDC Boards?
An SQDC board, representing Safety (S), Quality (Q), Delivery (D), and Cost (C), is a visual management tool used in manufacturing and operations. Comprising different columns, each dedicated to a specific element, the board serves as a centralized platform for teams to track and communicate key performance indicators related to safety, product quality, delivery schedules, and cost management.
By utilizing an SQDC board, organizations can enhance communication, streamline decision-making processes, and cultivate a culture of continuous improvement. This visual tool empowers teams to quickly identify and address issues related to safety incidents, product quality deviations, delivery challenges, and cost fluctuations, facilitating a more agile and responsive operational environment.
Learn about SQDC boards with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What are work instructions?
Work instructions are detailed step-by-step guides that provide clear directions on how to perform a specific task or job within an organization. These documents are crucial in various industries to ensure consistency, quality, and safety in the execution of work processes. Work instructions typically include information such as materials needed, tools required, sequential steps to follow, safety precautions, and any relevant quality standards.
Learn about Work Instructions with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is pareto analysis?
Pareto analysis, also known as the 80/20 rule or the Pareto principle, is a decision-making technique that suggests a large majority of problems (80%) are caused by a small number of root causes (20%). This principle is named after the Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto, who observed that 80% of the land in Italy was owned by 20% of the population. In the context of problem-solving or process improvement, Pareto analysis is used to identify and prioritize the most significant factors contributing to a problem or a set of issues.
Learn to conduct a pareto analysis with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is a spaghetti diagram?
A spaghetti diagram is a visual representation of the flow of people, materials, or information within a process or system. It gets its name because the lines that represent the flow often resemble a tangled mass of spaghetti, illustrating the complexity and inefficiencies in the workflow. This diagram is particularly useful in identifying and analyzing the physical movement and paths taken by individuals or objects in a given space.
Learn about Spaghetti diagram with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP

What is Andon?
Andon is a popular visual control tool for indicating issues or anomalies in the production process.
The word for a traditional paper lantern in Japanese is where the term "Andon" originates. Typically, an Andon system consists of a visual indicator, often a colored light or signal, and an accompanying alarm or alert.
Learn about Andon with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is the Pull System in Lean?
A key idea in the Lean approach is the Pull System, which centers on the idea of manufacturing products or providing services in response to real customer demand. In contrast to conventional push systems, which produce goods in advance of anticipated demand, the Pull System works by starting work only when necessary, usually in response to signals from end users or downstream operations.
Learn about Pull System with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
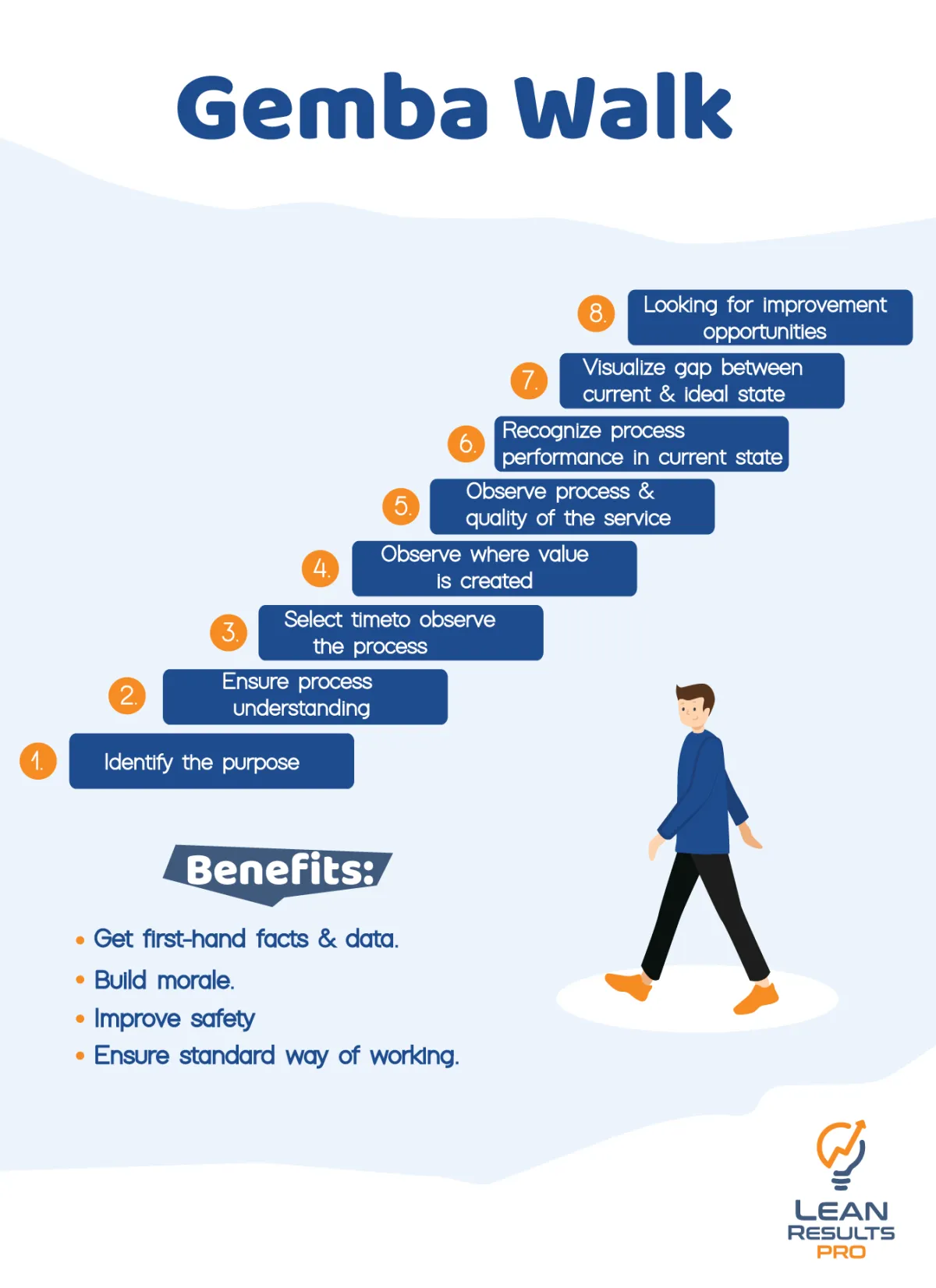
What is The Gemba Walk?
The Gemba walk, rooted in the principles of Lean culture, is a powerful management practice that involves leaders going to the actual workplace.
In Japanese, “Gemba” literally means “actual place” and its primary purpose of a
Gemba walk is for leaders to observe, engage with employees, and gain firsthand
knowledge about the current state of operations.
Learn about Gemba Walk with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is Value Stream Mapping?
A key Lean management tool for visualizing the entire process of delivering a product or service is Value Stream Mapping. VSM reveals the flow of materials, information, and activities through the use of visual representations, usually in the form of flowcharts. This allows for a thorough investigation of process efficiency. This approach identifies non-value-added tasks and draws attention to areas that could benefit from improvement.
Learn about Value Stream Mapping (VSM) with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is Heijunka?
Heijunka is a Lean manufacturing concept that aims to provide a constant and efficient production flow. It is also known as workload smoothing or production leveling. Heijunka aims to allocate output equally over a given period of time among various goods or services. This strategy prevents production bottlenecks and overstretching of certain resources while enabling firms to adapt more quickly to shifting consumer needs.
Learn about Heijunka with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
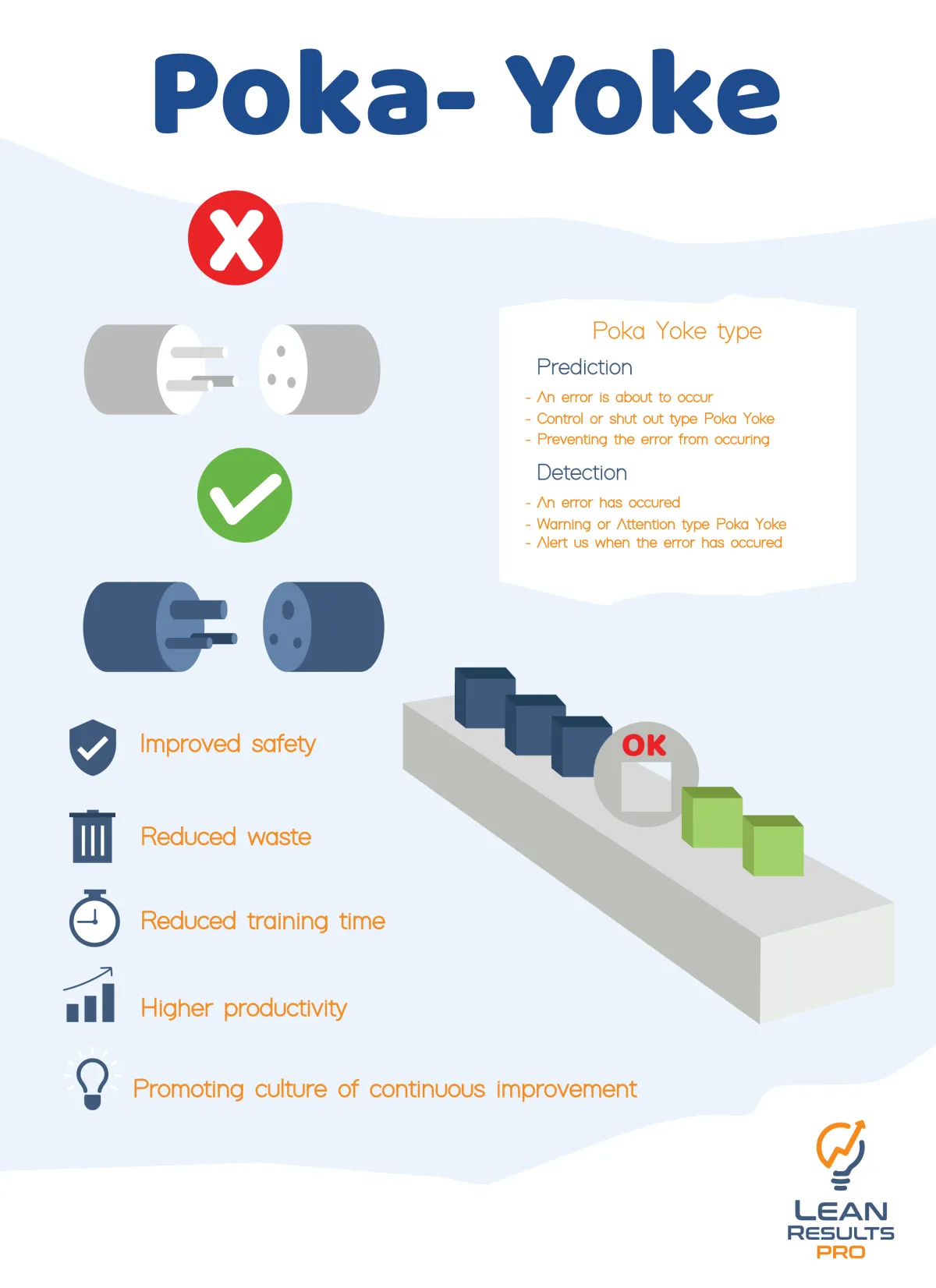
What is Poka-Yoke?
Mistake-proofing or "poka-yoke" in Japanese, is a Lean technique that aims to stop mistakes and flaws in processes.
The main goal is to create systems or procedures that are naturally error-proof or, in the event that errors do occur, detect them before they become flaws.
Learn about Poka-Yoke with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What are Tier Boards?
Tier Boards are an integral component of Lean methodology, designed to facilitate efficient communication, collaboration, and visual management within an organization. Also known as "Visual Management Boards" or "Tiered Accountability Boards," they play a crucial role in aligning teams and tracking progress toward organizational goals.
Tier Boards, in the context of Lean, are usually a series of strategically arranged visual displays arranged at various levels of hierarchy within a company. Teams can remain focused on goals and make data-driven choices by using these boards, which provide a real-time overview of important performance metrics, project statuses, and targets.
Learn about Tier Boards with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is Root Causa Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic problem-solving technique aimed at identifying the primary underlying factors that contribute to an issue or problem. In various industries, RCA is employed to understand the fundamental causes of problems rather than just addressing their symptoms. To find the underlying causes, a comprehensive investigation, data collection, and analysis process are required.
Learn about Root Cause Analysis (RCA) with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
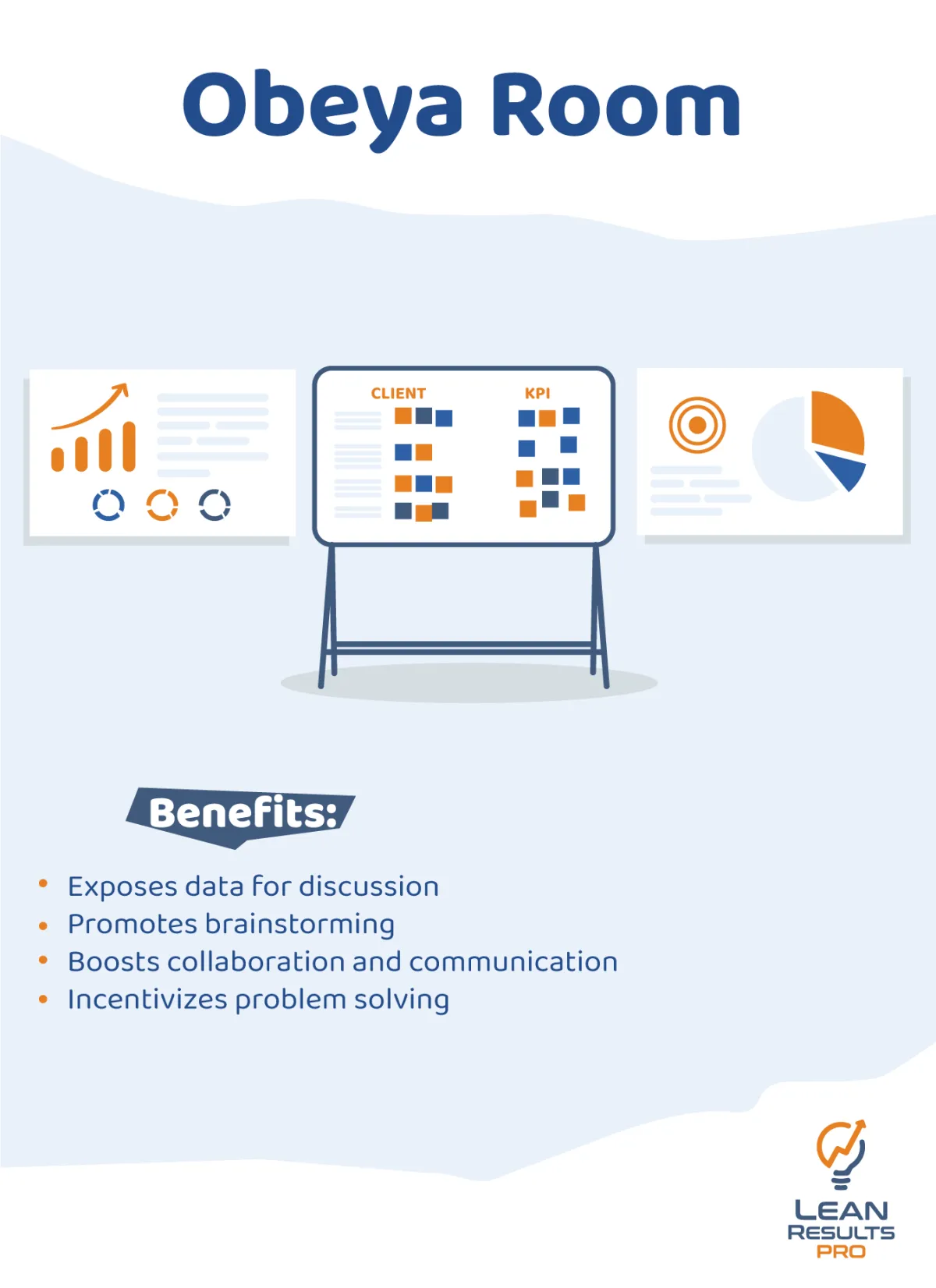
What is the Obeya Room?
The Obeya Room, also known as just "Obeya," is a potent Lean methodology idea that came from the Toyota Production System. In Japanese, "Obeya" means "big room" or "war room." It functions as a specific area, either real or virtual, created to support visual management, communication, and teamwork within a business.
Learn about Obeya Rooms with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is Mizusumashi?
Mizusumashi, a term derived from Japanese, translates to "water spider." Within the context of Lean methodology, Mizusumashi designates a key idea centered around logistics and material management. A Mizusumashi is a devoted worker that is frequently employed in manufacturing settings. Their job is to efficiently transport materials to the place of usage, guaranteeing a constant and uninterrupted flow of production. This idea minimizes waste related to inventory and transportation, which is in line with lean concepts.
Learn about Mizusumashi with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
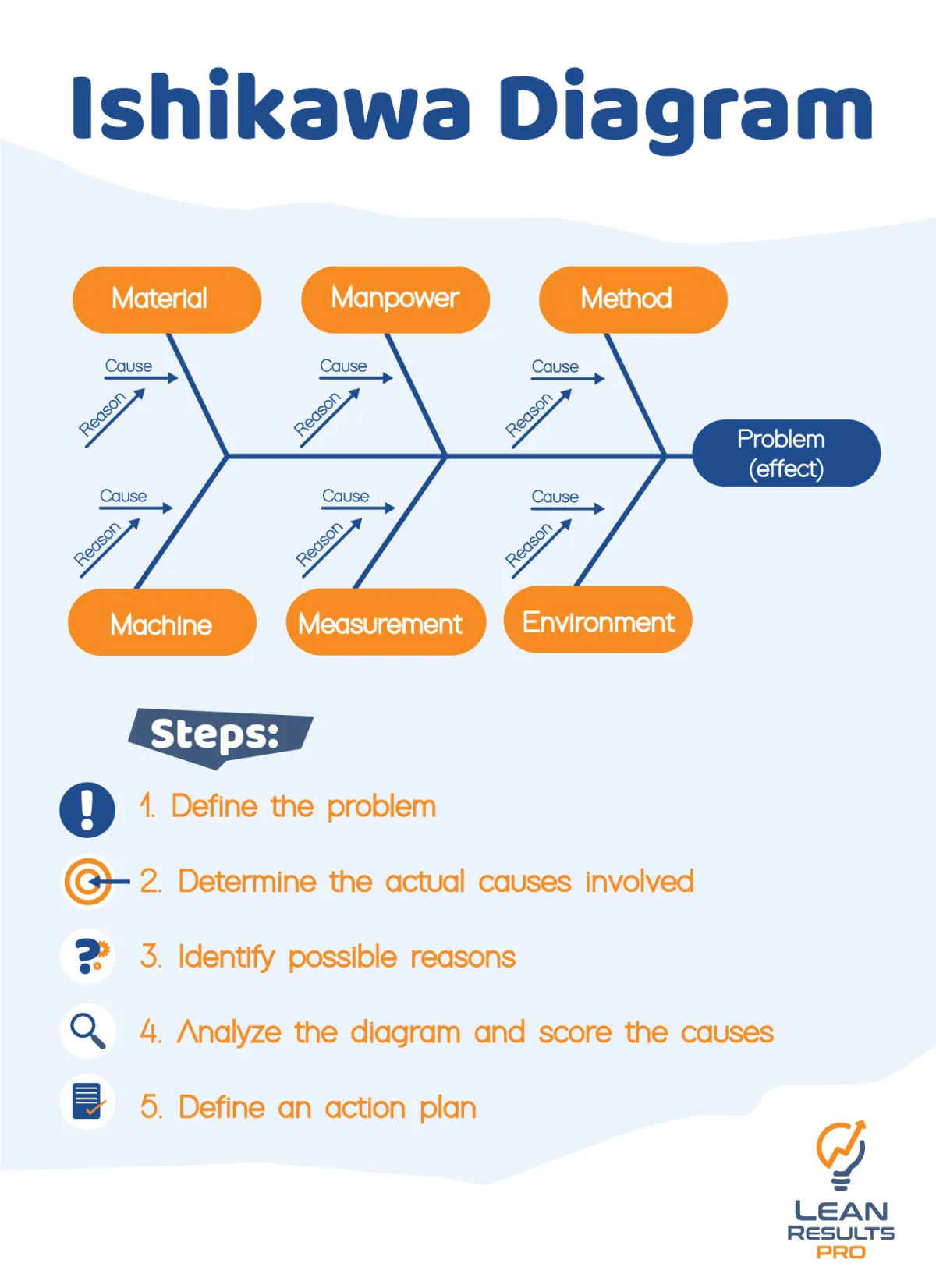
What is an Ishikawa Diagram?
In Lean problem-solving techniques, the Ishikawa Diagram, often called a Fishbone Diagram, is a crucial tool. Through collaborative problem-solving within the lean framework, teams may systematically discover and categorize the sources of specific difficulties thanks to this visual representation.
The graphic, which has a fishbone-like appearance, offers an organized and unambiguous method for comprehending contributing components. Organizations can utilize Ishikawa Diagrams to identify core problems and put effective remedies in place.
Learn about Ishikawa Diagram with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is Preventive Maintenance in Lean Culture?
In the context of lean procedures , while PM (Preventive Maintenance) is a typical group of tasks for the maintenance team, the other component, AM (Autonomous Maintenance), is composed by a group of tasks performed by the production team. Together they are commonly called as AM/PM. By carefully carrying out planned and routine maintenance, companies prevent unplanned malfunctions, maximize productivity, and prolong the life of their equipment.
Learn about Preventive Maintenance with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is a Leader in the Context of Lean Culture?
In the context of lean culture, a leader is not only a positional figure; rather, they are an innovator and a driving force behind ongoing development. Within the framework of lean approaches, a leader exemplifies servant leadership, cultivating a climate that supports responsibility, empowerment, and teamwork. Beyond traditional hierarchical positions, a lean leader creates a feeling of purpose and unites team members around a similar vision.
Learn about Lean Culture Leaders with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
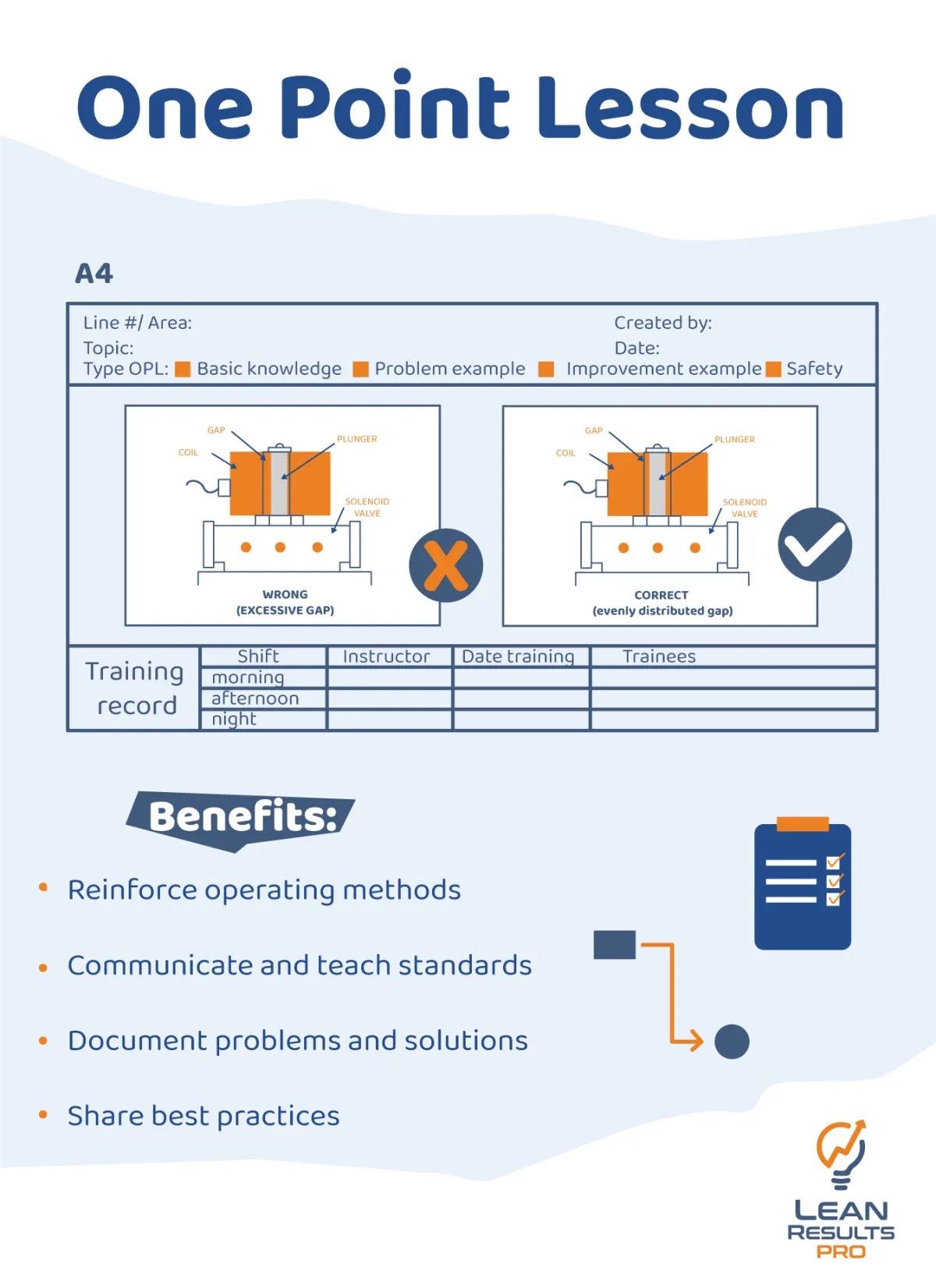
What is a One-Point Lesson?
A One-Point Lesson goes beyond traditional training aids, presenting itself as a succinct but effective tool that can quickly distribute critical knowledge throughout the vast terrain of lean culture.
This one-document resource is a dynamic enabler that speeds up the transfer of knowledge and makes a substantial contribution to process standardization, improved employee training, and the maintenance of a continuous improvement culture.
Learn about One-Point lessons with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
Why is Lean important?
Lean methodology plays a crucial role in helping organizations improve efficiency, reduce waste, enhance quality, and ultimately, deliver greater value to customers. Some key reasons why Lean is important include:
· Increased productivity and profitability
· Improved customer satisfaction and loyalty
· Reduced lead times and cycle times
· Lower operating costs and higher competitiveness
· Empowered and engaged workforce (through simplified daily tasks)
· Sustainable growth and resilience to market changes
· Continuous innovation and process improvement
Learn about Lean Management with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What are the Advantages of Lean?
Embracing Lean methodologies offers several key advantages that can significantly impact an organization's performance and competitiveness, some of these benefits are:
·Increased Efficiency: Lean methodologies focus on eliminating waste and optimizing processes, leading to greater efficiency and productivity. By streamlining workflows and reducing unnecessary activities, organizations can accomplish more with fewer resources and in less time.
·Improved Quality: Through the pursuit of perfection and continuous improvement, Lean methodologies emphasize delivering products and services of the highest quality. By standardizing processes, identifying and addressing defects, and empowering employees to take ownership of quality, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
·Reduced Costs: By eliminating waste and inefficiencies, Lean methodologies help organizations reduce operating costs and improve their bottom line. By optimizing processes, minimizing inventory, and maximizing resource utilization, organizations can achieve significant cost savings while delivering value to customers.
Learn about the Advzntages of Lean with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
How to promote a Lean Culture?
To promote a Lean culture effectively within your organization, it's essential to cultivate an environment that values continuous improvement and waste reduction. T
By implementing fostering a culture of Lean, organizations can drive continuous improvement, enhance efficiency, and achieve sustainable growth.
Learn about Lean Culture with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
How Lean Manufacturing works?
Lean manufacturing operates on the principle of waste reduction and process optimization. By identifying and eliminating inefficiencies and by simplifying processes, it enhances productivity and quality while reducing costs.
Techniques like Just-in-Time production, value stream mapping, and continuous flow manufacturing are commonly employed to achieve lean objectives. Through a systematic approach to resource utilization and workflow management, lean methodologies streamline operations across diverse industries.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What are Lean Manufacturing examples?
Examples of Lean manufacturing abound in various sectors. Companies like Toyota exemplify Lean principles through practices such as Just-in-Time inventory management and Kanban systems.
Other industries, including healthcare and hospitality, apply lean methodologies to improve service delivery and operational efficiency. By embracing lean concepts like standardized work and continuous improvement, organizations achieve greater responsiveness to customer needs and enhanced competitiveness.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What are Lean Manufacturing Principles?
Lean manufacturing principles revolve around eliminating waste, empowering employees, and optimizing processes. These principles include identifying and reducing eight types of waste, fostering a culture of continuous improvement, and respecting people's contributions .
By focusing on customer value and systematically improving workflows, lean organizations enhance efficiency and quality while minimizing costs. These principles, derived from Toyota's Production System, serve as the foundation for successful lean implementations across industries.
What are some successful Lean Implementations?
Numerous companies across various industries have achieved remarkable success through the implementation of Lean principles. For instance:
·Toyota: Often cited as the pioneer of Lean manufacturing, Toyota has continuously refined its production processes to maximize efficiency, minimize waste, and deliver high-quality vehicles to customers worldwide.
·General Electric: By adopting Lean methodologies, GE has streamlined its manufacturing operations, reduced lead times, and improved product quality, resulting in significant cost savings and enhanced customer satisfaction.
·Amazon: Known for its relentless focus on efficiency and customer satisfaction, Amazon has implemented Lean principles throughout its fulfillment centers, enabling the company to deliver millions of products to customers with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
Learn about Lean Implementations with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
How does Lean contribute to waste reduction and increased efficiency?
Lean methodologies play a crucial role in waste reduction and efficiency improvement by targeting eight types of waste commonly found in manufacturing processes.
By identifying and eliminating these forms of waste, Lean methodologies enable organizations to optimize processes, streamline workflows, and deliver greater value to customers with fewer resources and reduced costs.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
How can Lean principles be applied beyond manufacturing to other industries?
Lean principles, initially developed in manufacturing, have proven to be highly adaptable and applicable across a wide range of industries beyond manufacturing. Here's how Lean principles can be effectively applied in various sectors:
·Healthcare: In healthcare, Lean principles can improve patient care by streamlining processes, reducing wait times, and enhancing the overall patient experience. Hospitals and clinics can apply Lean methodologies to optimize scheduling, reduce medical errors, and eliminate waste in administrative tasks, leading to better patient outcomes and increased staff satisfaction .
·Service Sector: Lean principles are also valuable in service industries such as banking, hospitality, and retail. Organizations can use Lean techniques to improve customer service, enhance operational efficiency, and eliminate bottlenecks in service delivery. For example, banks can apply Lean methodologies to streamline account opening processes, reduce paperwork, and expedite customer transactions, resulting in faster service and improved customer satisfaction.
·Information Technology (IT): Lean principles can help IT organizations deliver projects more efficiently, reduce software development cycle times, and improve the quality of software products. By adopting Lean practices such as Agile development and DevOps, IT teams can enhance collaboration, increase productivity, and respond more effectively to changing customer needs and market demands.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What are Cross-Functional Teams??
Cross-functional teams are groups of individuals from different departments or areas of expertise who come together to work on a specific project or achieve a common goal. In Lean methodology, these teams play a crucial role in fostering collaboration, innovation, and efficiency.
Importance in Lean:
-Holistic Problem Solving: Cross-functional teams bring diverse perspectives and expertise, enabling comprehensive problem-solving and decision-making.
-Improved Communication: By breaking down silos, these teams enhance communication and coordination across the organization.
-Faster Implementation: With representatives from various functions, cross-functional teams can implement Lean initiatives more quickly and effectively.
Learn about Cross-Functional Teams with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What are Common Misconceptions About Lean?
1. Lean is Only for Manufacturing: While Lean originated in manufacturing, its principles are applicable across various industries, including healthcare, finance, and software development.
2. Lean Equals Cost Cutting: Lean focuses on value creation and waste reduction, not just cost cutting. The goal is to improve overall efficiency and quality, which may involve investments in training and new processes.
3. Lean is a Set of Tools: Lean is more than just a collection of tools; it is a philosophy and culture of continuous improvement that involves everyone in the organization.
4. Lean is About Working Faster: Lean aims to create value by improving processes and reducing waste, not just speeding up work. It emphasizes quality and efficiency over mere speed.
5. Lean is Only for Large Organizations: Lean principles can benefit organizations of all sizes by improving processes, reducing waste, and increasing customer satisfaction.
Learn about Lean Management with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
How Does Lean Contribute to a Company's Advantage?
Lean methodology significantly enhances a company's competitive edge by increasing efficiency, improving quality, and focusing on customer satisfaction. Lean streamlines processes, eliminates waste, and optimizes resource utilization, resulting in cost savings and higher productivity. This efficiency allows companies to deliver products faster to market, outpacing competitors.
Lean also fosters a culture of employee engagement and empowerment, encouraging innovation and continuous improvement. This cultural shift not only improves
operational performance but also boosts employee morale and retention. Additionally, Lean’s emphasis on waste reduction supports more sustainable practices, aligning with environmental and social responsibility goals. Together, these factors create a robust competitive advantage in today’s dynamic market.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is Jidoka?
Jidoka is a fundamental principle of Lean methodology that emphasizes quality at the source by enabling immediate detection and correction of defects. This concept ensures that issues are addressed as soon as they occur, preventing defective products from advancing through the production process.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What Lessons Can Be Learned from Failed Lean Implementations?
Failed Lean implementations offer valuable lessons that can guide future efforts to ensure success. Examining specific examples of failed implementations can
provide concrete insights:
-Nissan’s Early Lean Attempts: In the early 2000s, Nissan attempted to implement Lean practices without full leadership support and proper training. The company focused heavily on reducing costs without truly embedding Lean principles across the organization. As a result, the initiative led to short-term cost reductions but failed to achieve sustainable improvements. The lack of a Lean culture and insufficient training on Lean tools and methodologies were significant factors in the failure.
-General Motors (GM) in the 1980s: General Motors attempted to implement Lean practices inspired by Toyota’s production system. However, GM’s effort largely failed because it didn’t involve the workforce in the transformation. The company focused on Lean tools without fostering a culture of continuous improvement and worker empowerment. This top-down approach resulted in resistance from employees and superficial changes that didn’t lead to long-term benefits.
Lessons Learned:
1. Ensure Leadership Commitment: Successful Lean implementation requires strong and sustained support from top management. Leadership must be visibly committed and involved, as seen in the failures of Nissan and GM where leadership did not adequately support or understand Lean principles.
2. Invest in Training and Education: Comprehensive training on Lean principles and tools is essential. Employees at all levels need to understand Lean to apply it effectively. Nissan’s failure highlights the importance of proper training and education in Lean methodologies.
3. Foster a Lean Culture: Lean is not just a set of tools but a cultural shift. Encouraging a mindset of continuous improvement and involving employees in the process is crucial. GM’s experience shows that without a supportive Lean culture, tool-focused implementations fall short.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is Lean Auditing?
Lean auditing is a systematic approach to evaluating and improving an organization’s adherence to Lean principles and practices. It involves assessing how effectively Lean methodologies are being implemented and identifying areas for improvement. Lean auditing helps ensure that Lean initiatives are delivering the intended benefits and that continuous improvement is being sustained.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What is the Lean Maturity Model?
The Lean Maturity Model is a framework that helps organizations assess and understand their progress in implementing Lean principles. It provides a structured way to evaluate how well Lean practices are integrated into an organization’s culture and operations. The model typically consists of several stages, each representing a different level of Lean maturity. These stages help organizations identify where they are on their Lean journey and what steps they need to take to advance to the next level.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
What are some KPIs used to measure success?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential metrics used to evaluate the effectiveness and progress of Lean initiatives within an organization. Some common KPIs associated with Lean implementations include:
·Lead Time: The time it takes for a product or service to move through the entire value stream, from initial request to delivery to the customer. Reduced lead times indicate improved efficiency and responsiveness to customer demand.
·Cycle Time: The time it takes to complete a single process or task within the production or service delivery process. Shorter cycle times often indicate streamlined processes and increased productivity.
·Defect Rate: The percentage of products or services that fail to meet quality standards or customer requirements. A lower defect rate reflects improved quality and reduced waste in production processes.
·Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): A measure of equipment efficiency that considers availability, performance, and quality. High OEE scores indicate optimal equipment utilization and minimal downtime.
·Inventory Turnover: The rate at which inventory is bought, used, and replenished within a given period. Higher inventory turnover ratios indicate more efficient inventory management practices and reduced excess inventory levels.
Learn about Lean Manufacturing with the Lean Results PRO course.
And visit our youtube channel: www.youtube.com/@LeanCube-LRP
Learn how to implement the methods above with the Lean Results PRO course.



Copyright 2023 All Rights Reserved
